Why An Adult Dog Loses Its Teeth

When an adult dog loses its teeth, it is usually because the natural course of its life is approaching seniority. However, poor hygiene habits or severe gum disease can speed up the process.
Just like humans , older dogs are more prone to disease. Obesity, lack of energy, eye problems or mouth problems are some of the most common.
An adult dog with full dentition has 20 upper and 22 lower teeth. However , complete maintenance of dogs’ teeth is usually rare, as the practice of preventive oral hygiene in pets is not yet very widespread among owners.
Once an adult dog loses its teeth, stronger veterinary inspection is needed. This can prevent possible infection or even the loss of additional teeth.
The job of the specialist is very important, but the dedication of the owner to provide for a routine examination and cleaning of the teeth is key to the animal’s welfare.
Factors that weaken the dog’s teeth
Although dental problems can occur at any stage of life, they tend to occur more frequently with age. This is because the condition in question is compounded by natural physical wear and tear and the result of potentially poor preventive care.
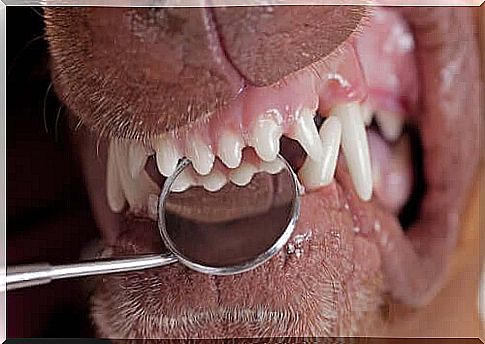
Some of the factors that increase tooth loss are:
- Gingivitis. Irritation and inflammation of the gums from bacterial plaque. It is usually caused by poor oral hygiene, although genetic or dietary factors can play a role. In the early stages it does not affect the teeth; it can even be reversed with a deep tooth cleaning. If left untreated, it leads to what is known as periodontal disease, in addition to worsening mouth odor and general pain.
- Periodontal disease. The tissue damage gets worse, so the infection spreads to the ligaments and bones of the teeth. It usually occurs after long periods of bacterial plaque, tartar, or poorly treated gingivitis, usually in dogs four to six years of age. Their irreversibility, which leads to the permanent loss of the gums, causes the dog to lose its teeth if improperly treated.
- Endodontic disease. A condition that weakens the inside of the tooth as a result of external trauma, abnormalities in tooth enamel, or tooth decay . Reddish or purple teeth and pain or swelling of the face are some of the most common symptoms that can lead to dental fistulas.

- Other factors. Unusual tooth development, such as a wrong bite or incorrectly developed teeth, the quality of the tooth enamel, or the wrong diet can be harmful to dental health. In addition, genetic factors, or even certain small breeds, are more prone to tooth loss.
What to do when an adult dog loses its teeth
It often goes unnoticed when a dog loses its teeth. Often times, when the teeth are not of considerable size or there are no obvious symptoms, owners do not seek treatment or correction for tooth loss in their pets.
If one or two teeth are affected, vets generally recommend strict hygiene, regular checkups, and tartar cleaning to prevent buildup.
In some cases , poorly treated infections can spread and weaken important structures.
If there are multiple “loose” teeth or other injuries that make feeding the animal difficult, experts will consider surgery or appropriate dietary changes.
Careful maintenance of a young dog’s dental health can determine their quality of life in adulthood. Therefore, hygienic care by the owner, along with proper nutrition and veterinary control, form the basic principles for the well-being of the animal.








