Breathing Difficulties In Cats: Causes And Symptoms

Difficulty breathing in cats is a common occurrence in veterinary emergency services. They can develop slowly or come on suddenly and without warning.
It is important to understand that breathing difficulties can be very distressing for your pet. They also run the risk of getting worse quickly, putting your pet’s life at risk.
Therefore , any animal with breathing problems should be treated as an emergency and carefully monitored while the diagnosis is made and treatment is administered.
Difficulty breathing in cats: what are the symptoms?
Difficulty breathing or dyspnea can manifest itself in many different ways. The patient may experience persistent coughing, loud breathing, a change in voice, or decreased mobility. Some of the more serious signs of difficulty breathing include:
- In addition to the obvious difficulty breathing in and out, cats with dyspnea often display a variety of associated clinical symptoms. For example, your breathing rate can be remarkably fast.
- They also often wheeze and cough with their mouths open. In addition, cats stretch their bodies forward and lower their heads at the same time, as if they were about to throw up. If the breathing difficulties are very severe, they may have blue gums due to lack of oxygen and, in the worst case, they may collapse.
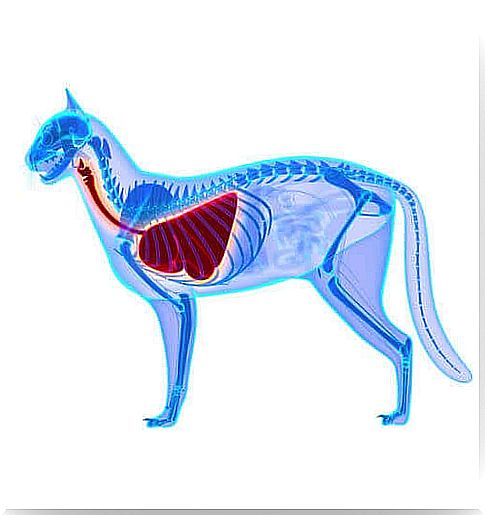
Common causes of breathing difficulties in cats
Difficulty breathing in cats can occur for many different reasons. Some of the most common causes are as follows:
- Asthma: In this condition, the airways become inflamed and convulsions occur. As a result, the airways narrow and cause severe breathing difficulties.
- Pneumonia: This is an infection of the lungs. It can be caused by various infectious agents or by bronchial aspiration. The latter can be caused by inhalation of food or liquids, after vomiting or belching.
- Congestive heart failure: Heart failure can cause fluid to build up in and around the lungs.
- Pleural effusion: This is a build-up of fluid in the lungs that makes it difficult for the cat to expand its chest. Often infections or even cancer are the cause of such effusions.
- Larynx paralysis: When the neck muscles are not working properly, laryngeal paralysis can occur. This prevents the cat’s larynx from opening to allow the air it needs to flow in.
- Other causes: Foreign bodies in the nostrils or windpipe and injuries in the chest can also cause breathing problems in cats.
There are many other causes of breathing difficulties as well.
Treatment and prognosis
As you can see, there are many different causes of breathing difficulties in cats, and they vary in severity. Therefore, the treatment and prognosis are very different depending on the cause and trigger of the breathing difficulties.
Most animals with breathing difficulties are treated with oxygen. This therapy can be carried out in different ways. This largely depends on the size of the patient and the general condition of the cat.
If your cat is very agitated and restless, the vet can also provide sedation. This supports your animal in coping with stress. If the cat’s condition is very serious and potentially life threatening, additional emergency measures or therapy may be needed to stabilize the cat.
These measures include draining fluid from the lungs or thoracentesis. It may also be necessary to make what is known as a trachea incision, which allows your animal to breathe if an object is stuck in the windpipe.
Setting up a fan can also help make it easier for your cat to breathe. However, the selection of the appropriate treatment and approach depends very much on the individual case.
Cats with difficulty breathing: research methods
For example, the vet can do blood tests, x-rays, computed tomography (CT), or ultrasound. In addition, there are other procedures such as bronchoscopy and cleaning the airways, which are performed under general anesthesia.
If your cat is having difficulty breathing, act quickly and see a veterinarian immediately.