Leptospirosis In Cats: Symptoms And Treatment

Leptospirosis in cats is a zoonotic disease of bacterial origin. Today, leptospirosis is viewed as an emerging infectious disease in humans and dogs.
However, there are a number of wild and domesticated animals – such as cats – that, despite being infected, show no symptoms of the disease. In these cases one speaks of a subclinical infection.
Animal species that carry this disease function as reservoirs for the bacteria and are a potential source of infection for other hosts and humans.
What we should know about the culprit: Leptospira
Zoonotic diseases are those that can be passed between different species of mammals. So they are diseases that are transmitted between humans and other animals.
To date, 22 species of Leptospira have been identified. 13 of them can trigger the disease in humans.
The Leptospira species are also classified according to their clumping reaction to sera that have antibodies that recognize the bacteria. This type of classification is called serotypes. About 300 pathogenic serotypes of Leptospira are known to date .
The shape of this bacterium is very characteristic: it is thin spirals. Usually both or one end of the organism are bent into a hook shape.
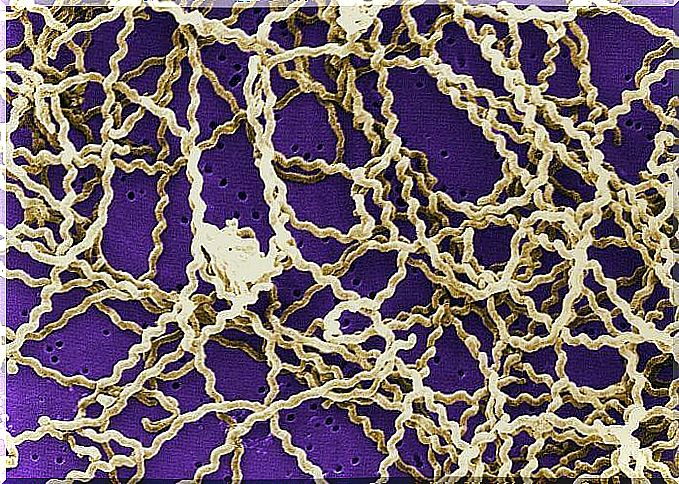
This bacterium enters the organism through contact. It penetrates through the skin and mucous membranes. This is due to the production of an enzyme that changes the permeability of connective tissues. It digests the hyaluronic acid content to make it easier to penetrate.
Leptospirosis in cats: how does the bacterium spread?
The bacterium is expelled through the urine of infected animals. The infected urine can contaminate surface water such as swamps, streams and rivers. The bacteria can survive in this habitat for several months. That is why we often transmit the disease through water.
Cats can acquire the infection directly or indirectly. In the case of indirect transmission, infection can occur through eating a wild animal that has drunk infected water.
In the direct transmission of leptospirosis in cats, the velvet paw has come into contact with the infected urine of other infected animals that live with the cat. Even if the cat drinks infected water, it can become infected.
After penetrating the mucous membranes or the skin , the leptospira multiply rapidly in the blood. The bacteria can affect many organs, especially the kidneys, where the leptospira can live and spread through the urine for months or years.
Signs and symptoms of leptospirosis in cats
When infected cats are analyzed, the bacteria are found in the urine and blood. These studies have shown that leptospirosis produces only mild clinical signs in cats .
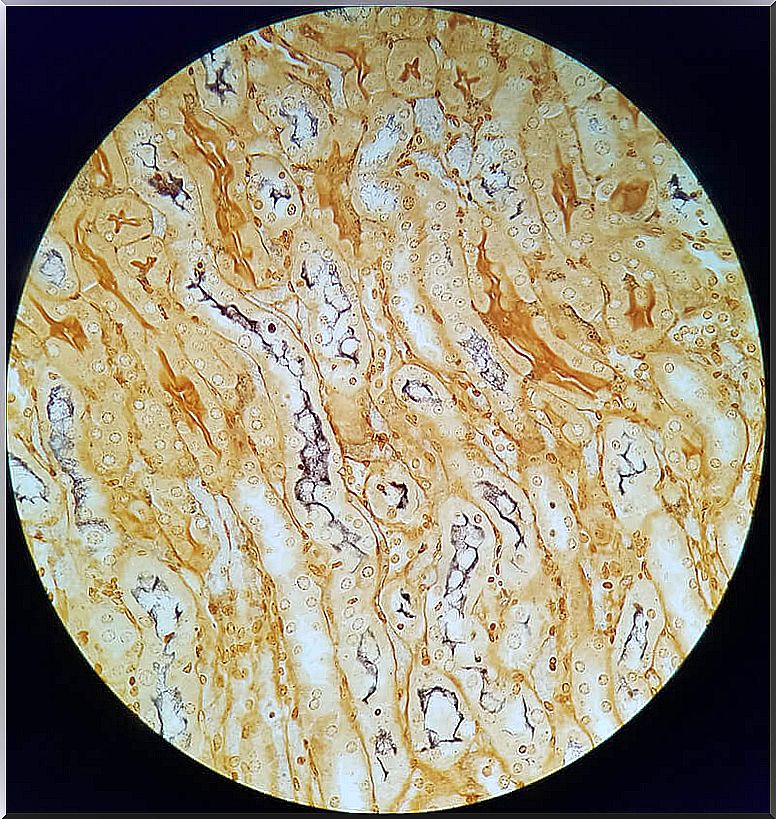
Although clinical signs are rare in cats, leptospirosis causes kidney and liver inflammation in cats. New studies have shown a possible link between chronic kidney inflammation in cats and infection by Leptospira spp .
Treatment of the disease
As with dogs, treatment for cats will depend on the severity of the clinical symptoms. The animals are usually given antibiotics and supportive therapy.
Cats that appear healthy and excrete leptospira in urine should be treated with doxycycline (5mg / kg) every 12 hours for three weeks to stop them being carriers.
Prevention of leptospirosis in cats
- Unfortunately there is no vaccination yet .
- The only way to avoid infection is to make sure the kitties are not eating potentially infected rodents. You also have to avoid them coming into contact with standing water.
- Pure house cats suffer from a very low risk of infection.
Take your cat to the vet to rule out the disease. Also, remember that your cat may not show symptoms, but it can still infect people and dogs around them.
We cannot imagine life without cats. But the fact that cats can be a reservoir for Leptospira in living quarters is important. Therefore one should have the animals examined in any case.
There are special samples that can identify the bacteria in the blood, urine or tissue. You can also have additional tests carried out to find antibodies against the bacteria in the cat’s blood.








