What Is A Generation Of Animals? The Effects Of Inbreeding

There are three key functions that define living things: nutrition, relationships, and reproduction. A living organism needs food to develop and stay alive. In addition, it has to come into contact with other individuals and with its environment and of course it has to reproduce and produce offspring. This then creates a new generation of animals within a population . It includes one or more young animals that are born as a result of the reproduction of the parent animals.
While this may seem pretty straightforward at first , each new generation of animals faces major challenges that may also differ from those of their parents.
Therefore, the genetics these animals receive from their parents, which in turn come from many previous generations, are key to their survival. Would you like to learn more about the characteristics and challenges of a generation of animals? Then just read on!
Dominant alleles and recessive alleles
When two animals mate and produce offspring, we expect that the young animals each carry half the genetic code of the mother and half of the father. In other words, you assume they are a mix of the two. However, it can often be observed that the offspring look more like one parent than the other. But why is that actually happening?
Dominant alleles and recessive alleles are found in the DNA. These alleles are the different alternatives of a gene. As a result , a generation of animals may exhibit physical characteristics that are unlike those of their parents.
For example, imagine two black rabbits with white offspring. But what exactly could have happened here? Well, maybe the gene that codes for black color in rabbits is a dominant allele. If the parents each had a dominant allele and a recessive allele in relation to hair color, then the color black will prevail.
In the present example, however, the gametes (egg cell and sperm) only carried the recessive allele during reproduction. Therefore, the offspring of these two black rabbits could only be born with white fur.
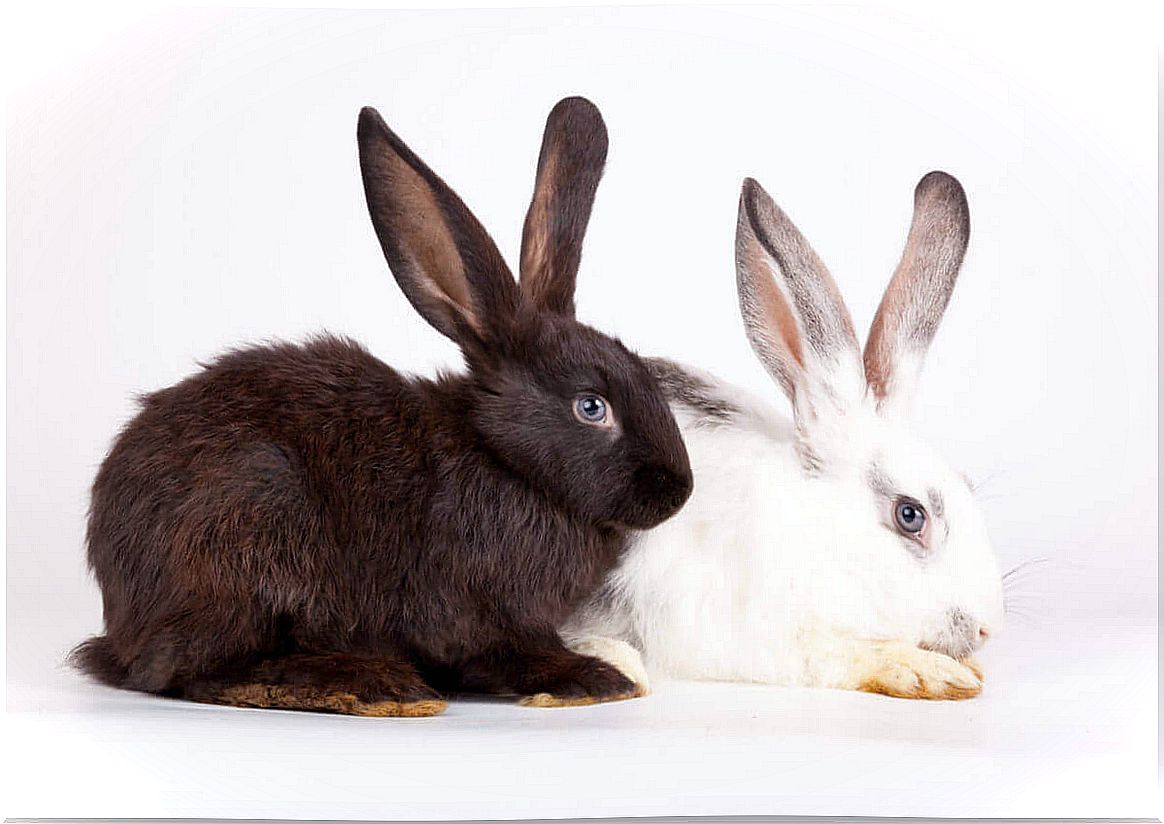

Now imagine that all the black rabbit parents disappear. For some reason this genetic information was lost. As a result, only white rabbits remain. Unfortunately, the white fur is not the best color, unless the rabbits live in the snow. This example shows very impressively and in detail how a genetic loss affects every generation of animals.
Animal generation, inbreeding and endangered animal species
Genetic diversity is key to the survival of any species as such. As this diversity in an animal population decreases, the risk that this species will disappear increases.
The number of alleles present in a population is a measure of genetic diversity. Because the more alleles are available, the greater the genetic diversity.
In addition, the frequency with which these alleles are produced in a population is another factor influencing their genetic diversity. Because small spontaneous mutations can increase the diversity of alleles over time.
This genetic diversity can increase with each new generation of animals. When extrapolated in terms of evolutionary time, this is one of the reasons why new species are emerging on the planet.
Causes of Inbreeding
One of the reasons animals are included on the Endangered Species List is inbreeding. However, deforestation, habitat destruction, fragmentation or uncontrolled hunting of these animals resulting in population isolation are the primary reasons for this fact. Rather, inbreeding is a consequence of these factors.
There are two types of inbreeding; one is accidental and unintentional, while the other is intentional. In the first case, the intentional mating of closely related animals such as siblings or parents and children leads to a drastic loss of genetic diversity. At the same time, genetic diseases or a lower resistance to pathogens occur.
This type of inbreeding occurs in wildlife when the number of individuals in a population has decreased due to a significant restriction in the available habitat. It also occurs in animals that have been isolated as a result of habitat fragmentation. These populations will become extinct over time.
On the other hand, there is accidental inbreeding as a result of genetic drift. Genetic drift is an evolutionary factor that, together with natural selection, causes changes in the frequency of alleles over the course of evolution.
If a species has a low allele frequency and all of its alleles for a gene are the same, any disturbance in the environment can cause that species to become extinct. Because of this, when humans destroy some aspect of their ecosystem, some species disappear faster than others.
Strategies to avoid inbreeding within an animal generation
In nature, each species in balanced ecosystems has its own strategies to avoid inbreeding and thus increase genetic diversity in each generation.
Some animal species, such as the lions, have a matrilineal hierarchy. This means that the females of each generation usually remain in the group while the males have to leave the group.
Every now and then a new male comes and kills all the young in order to get the females ready to conceive again. Although this may sound very cruel, it is precisely this behavior that ensures that the population receives new genetic information that leads to the strengthening of the species.
In other cases, the key to avoiding inbreeding is for the pups to move away from their parents and form new pairs with other populations. Large migrations are another good example of dispersive movements in bulk and over great distances.
In the end, large groups of individuals – who are genetically very different from one another – will gather together to find a partner and reproduce.
The destruction of the natural habitat of the animals leads to a reduction in the territories in which many species can settle. In addition, they practically no longer have the opportunity to find new places to settle and thus create a new generation of genetically diverse animals.
However, the extinction of a species is not the result of a single cause. Ultimately, it is not uncontrolled hunting that exterminates a species. Rather, the reason is the lack of a suitable habitat. As a result, the animals then have to mate with closely related conspecifics. And this in turn leads to a species becoming extinct.









